Why is scoliosis more common in girls?
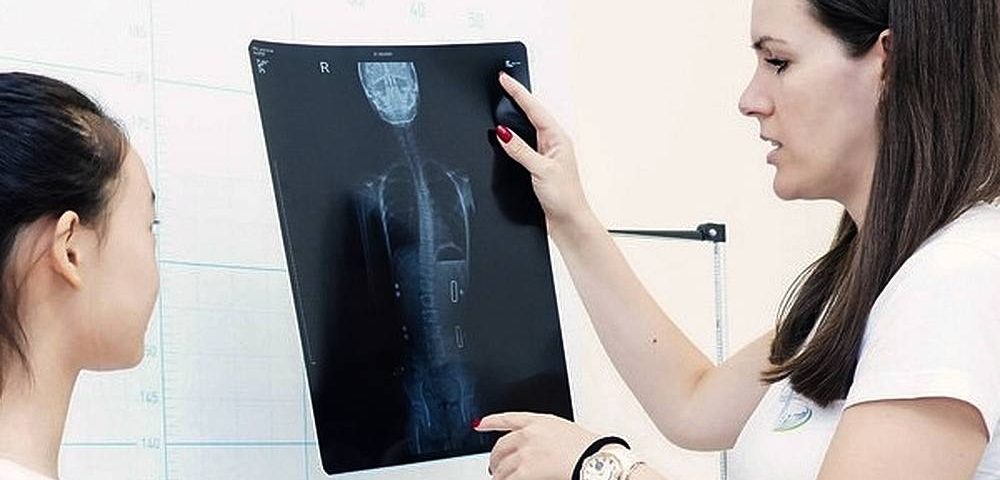
Scoliosis is the most complex deformity of the spine. When this deformity occurs, first the spine changes in the sagittal (lateral) plane, there is a loss of physiological lateral curves. In people who have scoliosis, reduced physiological kyphosis and lordosis are observed and this is called flatback. Around 80% of scoliosis belongs to the group of named idiopathic scoliosis. Although the cause of this type of scoliosis is unknown, we know that asymmetric loading and gravity lead to progression.
This deformity (adolescent idiopathic scoliosis) most often occurs in the prepubertal and pubertal period, and it significantly occurs more in girls than in boys. Rapid growth
and development is the most critical period for the development of scoliosis and occurs earlier in girls than in boys.
In the period when the sudden growth starts, physiological curves like natural kyphosis and lordosis have not yet been formed in girls. In this phase of growth, due to the absence of sagittal curves, the spine is unstable and a perfect base is created for the possible occurrence of deformities.
The spinal column in this phase of growth is always in the position of a flat back and is always unstable, although that does not necessarily mean that scoliosis will occur.
For boys, the situation is a bit different compared to girls. Their sudden growth and development begins later in relation to girls, when the sagittal curves are already formed, and thus the possibility of scoliosis is reduced.
Knowing about different periods of growth and development gives us the answer to the question why adolescent idiopathic scoliosis as a deformity is more common in girls than boys.
